|
Otitis (Ears)

Middle Ear Fluid
Middle ear fluid build up could be a complication of having allergies or ear infections in children and adults. Fluid is normally produced in the middle ear (the space behind the eardrum) in small amounts. Usually the fluid drains out of the ear though the eustachian tube into the back of the nose. Ear fluid can cause a problem when it builds up in the middle ear. This condition is called otitis media with effusion, or secretory otitis media.
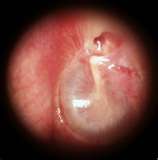
After an ear infection, the eustachian tube may be temporarily blocked and fluid will build up in the middle ear space instead of draining out normally. After taking antibiotics for the ear infection, your child may still have fluid left in the middle ear, but it is no longer infected fluid.
If there is fluid in the middle ear, your child will probably have:
► a full, congested sensation in the ear
► mildly reduced hearing (temporary).
► There could be off and on earache without fever.
If there is still fluid in the ear after 3 to 4 months, children and adults will need evaluation by an allergist to determine if allergies are contributing to impair drainage. If proper medical treatment dose not improve or resolve the fluid build up an Ears, Nose and Throat specialist evaluation may be required.
Control allergies
If your infant has a continuously runny nose, consider allergy as a contributing factor to the ear infections. If your child has other allergies such as eczema, your healthcare provider will check for a milk protein or soy protein allergy.
Adenoids
If your toddler constantly snores or breathes through his mouth, he may have large adenoids. Large adenoids can contribute to ear infections. Talk to your allergist about this.
|

